System administration

This groups all knobs that allow to manage and adapt the behavior of ARIS to the needs of the laboratory and user preferences. They are grouped in two to facilitate their access.
Generic[edit]
This groups all the basic administration functionalities. They are available for both the system administration and the laboratory supervisor.
Users[edit]
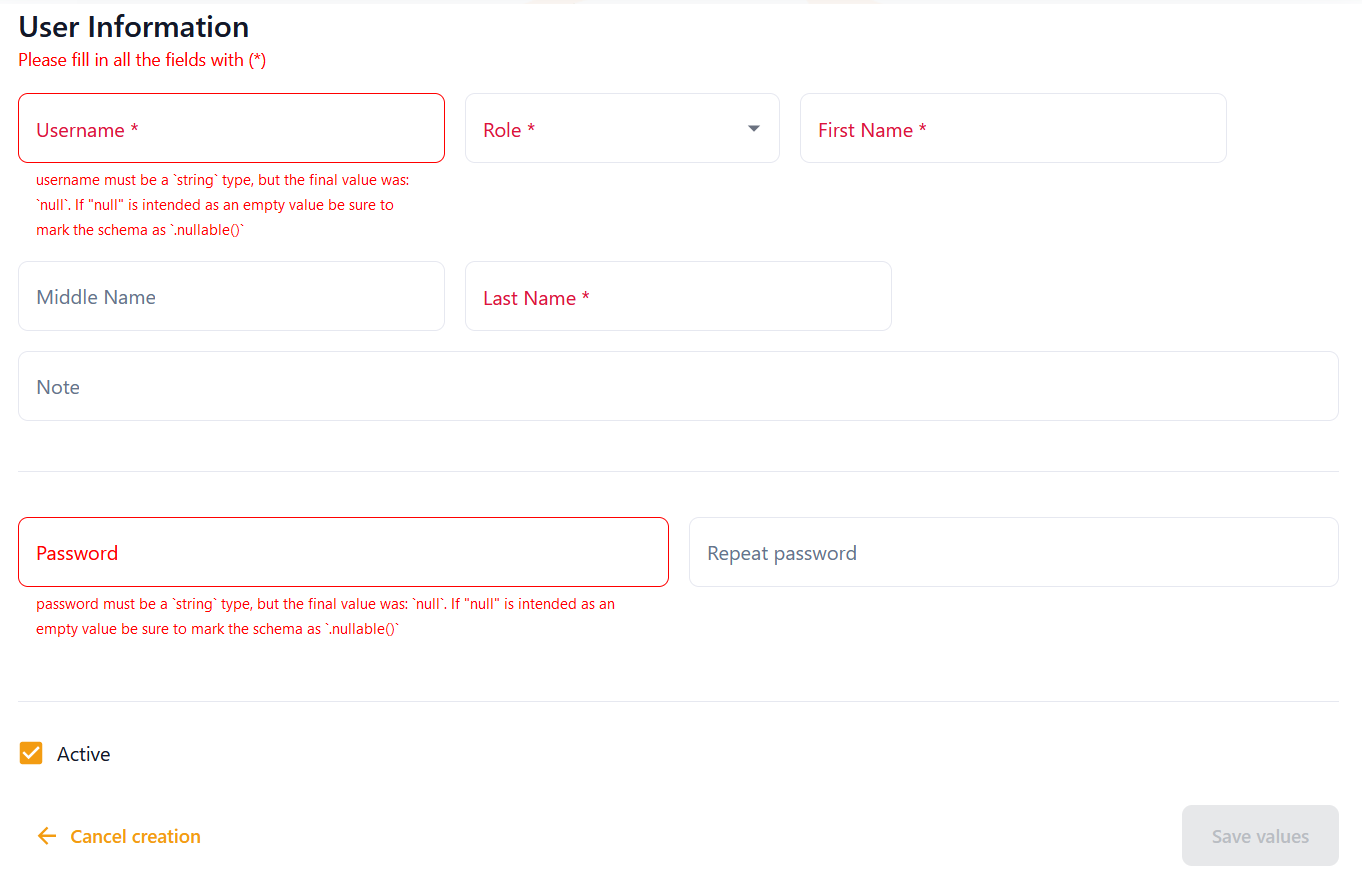
When clicking on the edit or New user buttons, a form pops up on the screen. The information necessary to create a user consists of a Username, Name, Middle name, password and the person's Role within the system. This Role will determine the functionalities available to the user. A note, without any effect in the behavior of the application can be added to indicate any relevant information to the system administrator.
This same form allows the system administrator to modify the password of any other user. For security reasons, this password must contain some number, some capital letter, some small letter, and at least eight characters.
Since they are used to audit changes in patients and requests, the users cannot be deleted from the system. However, they can be declared not to be active, which would prevent them from logging in, but still keep track in the database of all their past actions.
Access log[edit]
The access log shows the user which user has done an action within the system and exactly when. The timestamp is in the format Year-Month-Day Hour:Minute:Second
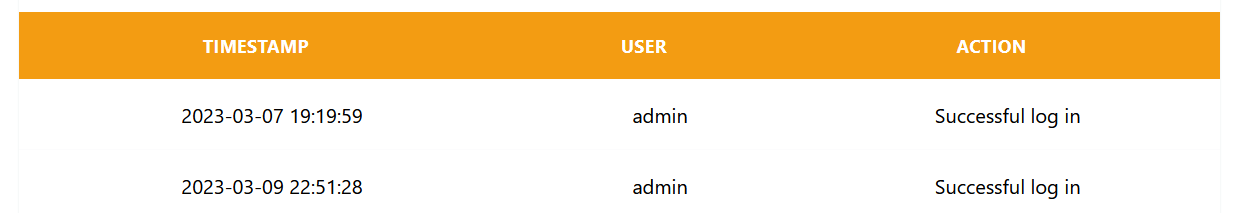
There are three actions recorded by the access log, successful log in, wrong user and failed log in. This last action refers to the wrong password being used.
Downloaded fields[edit]
ARIS allows the laboratory supervisor to download all the information in the database into a single file in their computer. There are two possible download options, depending of the format of the generated file being plain CSV, or compressed and password protected ZIP. These documents will contain information on the requests, and by extension, on the corresponding patients. Thus, due to patient confidentiality, not all of the personal data should be in the downloaded file. The checkboxes in this form allow the user to decide which fields will be downloaded in each one of the formats.
Technical[edit]
This groups all the more advanced administration functionalities. They are available only for the system administration.
Summary of instances[edit]
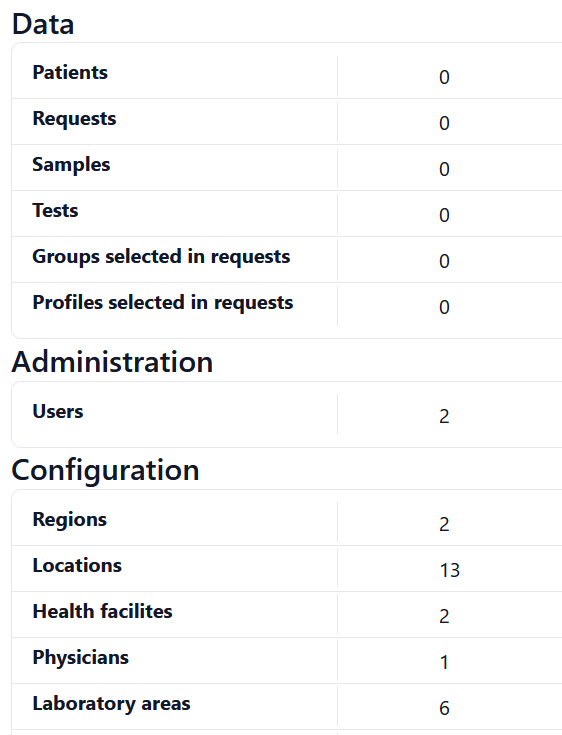
This tab displays information about the different existing instances in the application. Some examples are: the number of patients, users, requests or genders. This information comes directly from the database and is automatically updated after every modification in the system. It can be useful to investigate potential performance problems is case of extremely large numbers. To facilitate the reading and identification of the different kinds of instances, the information is divided into three sections: Data, Administration and Configuration.
Roles[edit]
This tab is displayed and works, in the same way as the State of the request tab in the Configuration functionality. The roles are unchangeable, but their labels (not the corresponding functionality) can be customized.
Each role has different actions allowed within the application, chosen due to the tasks the people are expected to carry out. Thus, there are three roles within the system, which indicate the functionalities that a user can perform, as can be seen in the following table.
Parameters[edit]
Parameters determine the behavior of some functionalities. Thus, they cannot be created or deleted. However, their values can be updated to customize the system. At this point it is important to highlight the on updating them, the data type must be respected. Providing a value of the wrong data type (e.g., a string instead of an integer) can provoke the malfunction of the whole application.
The following table contains the list of existing parameters together with the corresponding data type and a brief description.
| Name | Data type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| version | String | Version of the system |
| name | String | Caption to appear at the top of the screen, in the navigation bar |
| default_language | String | Language set by default on logging in (the same for all users) |
| timeout | Integer | Time (in minutes) after wich the connection to the backend requires a new log in |
| table_default_paging | Integer | This indicates the initial paging of all the tables (accepted values are 5, 10 or 25) |
| table_min_rows_for_search | Integer | This is the minimum number of rows a table must have to show the corresponding search field |
| attribute_reserved1 | String | Label of the first field of free use in the requests (write 'DoNotShow' to hide it) |
| attribute_reserved2 | String | Label of the second field of free use in the requests (write 'DoNotShow' to hide it) |
| attribute_reserved3 | String | Label of the third field of free use in the requests (write 'DoNotShow' to hide it) |
| filename_background | String | File containing the image displayed in the background |
| filename_sidebarlogo | String | File containing the logo displayed at the bottom of the sidebar |
| filename_favicon | String | Icon of the system used in the browser tab |
| bluetooth_enabler | String | Indicates the availability of automatic tests through Bluetooth connection (accepted values are 'Enabled' and 'Disabled') |
| zip_password | String | This is the password that will be used to generate the downloaded zip file |
| log_history | Integer | Maximum number of days to keep registries in the access log (those older than this will be automatically deleted) |
| backup_frequency | Integer | Minimum amount of hours that need to pass for the system to generate a new copy of the database |
| backup_history | Integer | Maximum number of copies of the database kept (once reached, oldest copy in the folder is deleted) |
| max_image_volume | Integer | Maximum number of megabytes used to store images (once reached, oldest ones in the folder are deleted) |
| filename_worklistlogo | String | Logo used in the worklist reports |